Fourth Grade Human Body!
Cells: OverviewCells are the Starting PointAll living organisms on Earth are divided in pieces called cells. There are smaller pieces to cells that include proteins andorganelles. There are also larger pieces called tissues andsystems. Cells are small compartments that hold all of the biological equipment necessary to keep an organism alive and successful on Earth.
A main purpose of a cell is toorganize. Cells hold a variety of pieces and each cell has a different set of functions. It is easier for an organism to grow and survive when cells are present. If you were only made of one cell, you would only be able to grow to a certain size. You don't find single cells that are as large as a cow. Also, if you were only one cell you couldn't have a nervous system, no muscles for movement, and using the internet would be out of the question. The trillions of cells in your body make your life possible. One Name, Many Types There are many types of cells. In biology class, you will usually work with plant-likecells and animal-like cells. We say animal-like because an animal type of cell could be anything from a tiny microorganism to a nerve cell in your brain. Plant cells are easier to identify because they have a protective structure called a cell wall made of cellulose. Plants have the wall; animals do not. Plants also have organelles like thechloroplast (the things that make them green) or large water-filled vacuoles. We said that there are many types of cells. Cells are unique to each type of organism. Humans may have hundreds of types of cells. Some cells are used to carry oxygen (O2) through the blood (red blood cells) and others might be specific to the heart. If you look at very simple organisms, you will discover cells that have no defined nucleus (prokaryotes) and other cells that have hundreds of nuclei (multinucleated). The thing they all have in common is that they are compartments surrounded by some type of membrane. Edible Cell Project: (Click here) |
|
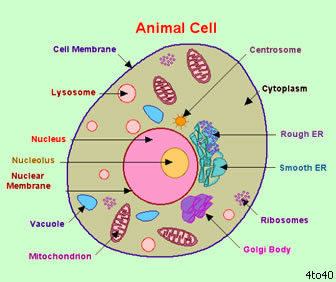
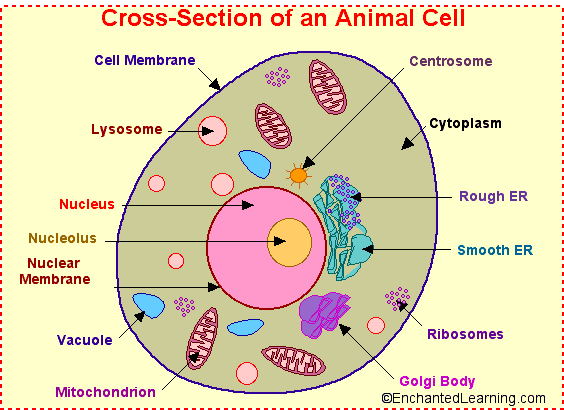
The following is a glossary of animal cell terms:
cell membrane - the thin layer of protein and fat that surrounds the cell. The cell membrane is semipermeable, allowing some substances to pass into the cell and blocking others. centrosome - (also called the "microtubule organizing center") a small body located near the nucleus - it has a dense center and radiating tubules. The centrosomes is where microtubules are made. During cell division (mitosis), the centrosome divides and the two parts move to opposite sides of the dividing cell. The centriole is the dense center of the centrosome. cytoplasm - the jellylike material outside the cell nucleus in which the organelles are located. Golgi body - (also called the Golgi apparatus or golgi complex) a flattened, layered, sac-like organelle that looks like a stack of pancakes and is located near the nucleus. It produces the membranes that surround the lysosomes. The Golgi body packages proteins and carbohydrates into membrane-bound vesicles for "export" from the cell. lysosome - (also called cell vesicles) round organelles surrounded by a membrane and containing digestive enzymes. This is where the digestion of cell nutrients takes place. mitochondrion - spherical to rod-shaped organelles with a double membrane. The inner membrane is infolded many times, forming a series of projections (called cristae). The mitochondrion converts the energy stored in glucose into ATP (adenosine triphosphate) for the cell. nuclear membrane - the membrane that surrounds the nucleus. nucleolus - an organelle within the nucleus - it is where ribosomal RNA is produced. Some cells have more than one nucleolus. nucleus - spherical body containing many organelles, including the nucleolus. The nucleus controls many of the functions of the cell (by controlling protein synthesis) and contains DNA (in chromosomes). The nucleus is surrounded by the nuclear membrane. ribosome - small organelles composed of RNA-rich cytoplasmic granules that are sites of protein synthesis. vacuole - fluid-filled, membrane-surrounded cavities inside a cell. The vacuole fills with food being digested and waste material that is on its way out of the cell. |
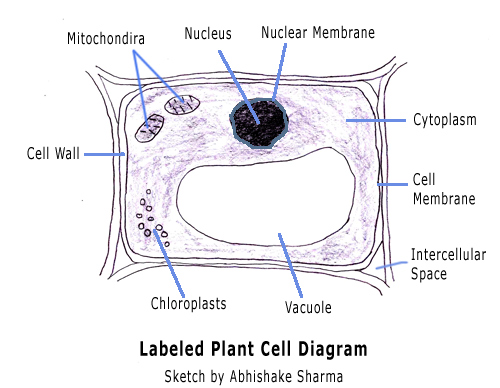
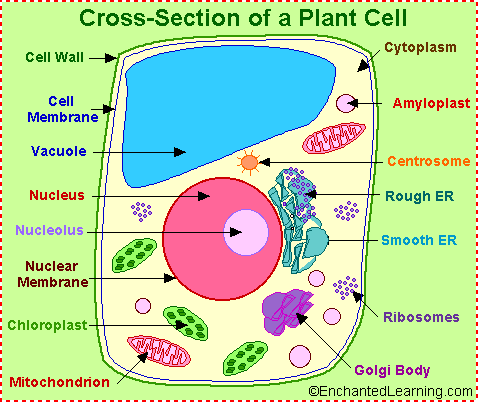
The following is a glossary of plant cell anatomy terms:
amyloplast - an organelle in some plant cells that stores starch. Amyloplasts are found in starchy plants like tubers and fruits. ATP - ATP is short for adenosine triphosphate; it is a high-energy molecule used for energy storage by organisms. In plant cells, ATP is produced in the cristae of mitochondria and chloroplasts. cell membrane - the thin layer of protein and fat that surrounds the cell, but is inside the cell wall. The cell membrane is semipermeable, allowing some substances to pass into the cell and blocking others. cell wall - a thick, rigid membrane that surrounds a plant cell. This layer of cellulose fiber gives the cell most of its support and structure. The cell wall also bonds with other cell walls to form the structure of the plant. chlorophyll - chlorophyll is a molecule that can use light energy from sunlight to turn water and carbon dioxide gas into sugar and oxygen (this process is called photosynthesis). Chlorophyll is magnesium based and is usually green. chloroplast - an elongated or disc-shaped organelle containing chlorophyll. Photosynthesis (in which energy from sunlight is converted into chemical energy - food) takes place in the chloroplasts. cytoplasm - the jellylike material outside the cell nucleus in which the organelles are located. Golgi body - (also called the golgi apparatus or golgi complex) a flattened, layered, sac-like organelle that looks like a stack of pancakes and is located near the nucleus. The golgi body packages proteins and carbohydrates into membrane-bound vesicles for "export" from the cell. mitochondrion - spherical to rod-shaped organelles with a double membrane. The inner membrane is infolded many times, forming a series of projections (called cristae). The mitochondrion converts the energy stored in glucose into ATP (adenosine triphosphate) for the cell. nuclear membrane - the membrane that surrounds the nucleus. nucleolus - an organelle within the nucleus - it is where ribosomal RNA is produced. nucleus - spherical body containing many organelles, including the nucleolus. The nucleus controls many of the functions of the cell (by controlling protein synthesis) and contains DNA (in chromosomes). The nucleus is surrounded by the nuclear membrane photosynthesis - a process in which plants convert sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into food energy (sugars and starches), oxygen and water.Chlorophyll or closely-related pigments (substances that color the plant) are essential to the photosynthetic process. ribosome - small organelles composed of RNA-rich cytoplasmic granules that are sites of protein synthesis. vacuole - a large, membrane-bound space within a plant cell that is filled with fluid. Most plant cells have a single vacuole that takes up much of the cell. It helps maintain the shape of the cell. |
|
|
|
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
|
Introductory Video
|
Vocabulary
respiratory trachea inhale exhale bronchial tube air sac diaphragm Working Model (Click here) (Assessment) |
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
|